Epigenetics
Epigenetics is the study of biological mechanisms that will switch genes on and off, to be put as a simplified definition. What does that mean? Well, if you are new to this whole thing, we first need a quick crash course in biochemistry and genetics before learning exactly what is epigenetics:
- Cells are fundamental working units of every human being. All the instructions required to direct their activities are contained within the chemical deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA.
- DNA from humans is made up of approximately 3 billion nucleotide bases. There are four fundamental types of bases that comprise DNA – adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine, commonly abbreviated as A, C, G, and T, respectively.
- The sequence, or the order, of the bases is what determines our life instructions. Interestingly enough, our DNA sequence is mostly similar to that of a chimpanzee. Only a fraction of distinctively different sequences makes us human.
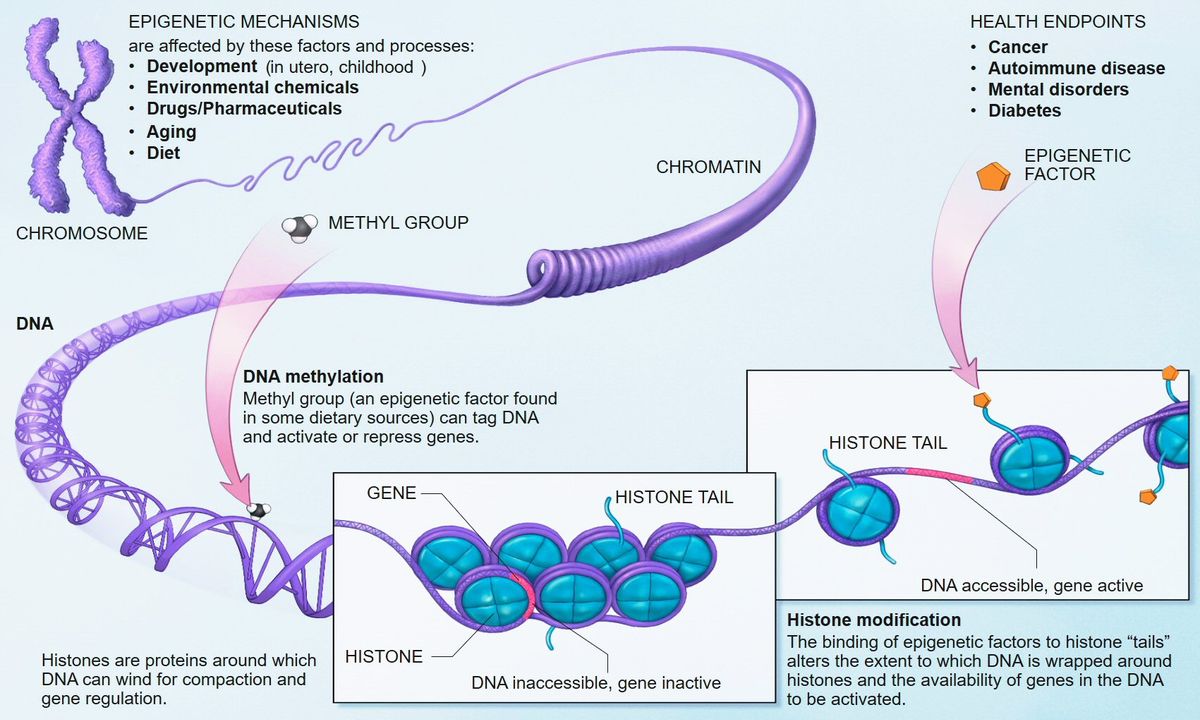
- Within the 3 billion bases, there are about 20,000 genes. Genes are specific sequences of bases that provide instructions on how to make important proteins – complex molecules that trigger various biological actions to carry out life functions.
In other words, DNA gives the instructions for various functional proteins to be produced inside the cell — this process is also known as the central dogma of molecular biology. Now that you understand genetics, let’s learn about epigenetics. Epigenetics affects how genes are read by cells, and subsequently whether the cells should produce relevant proteins. For example, the COL1A1 gene in DNA is present in all types of cells but “expressed” in skin cells to produce Type 1 Collagen proteins. Here are a few important points about epigenetics:
- Epigenetics Controls Genes. This is achieved through (a) nature: epigenetics is what determines a cell’s specialization (e.g., skin cell, blood cell, hair cell, liver cells, etc.) as a fetus develops into a baby through gene expression (active) or silencing (dormant); and (b) nurture: environmental stimuli can also cause genes to be turned off or turned on.
- Epigenetics Is Everywhere. What you eat, where you live, who you interact with, when you sleep, how you exercise, even aging – all of these can eventually cause chemical modifications around the genes that will turn those genes on or off over time. Additionally, in certain diseases such as cancer or Alzheimer’s, various genes will be switched into the opposite state, away from the normal/healthy state.
- Epigenetics Makes Us Unique. Even though we are all human, why do some of us have blonde hair or darker skin? Why do some of us hate the taste of mushrooms or eggplants? Why are some of us more sociable than others? The different combinations of genes that are turned on or off is what makes each one of us unique. Furthermore, there have been indications that some epigenetic changes can even be inherited.
- Epigenetics Is Reversible. With more than 20,000 genes, what will be the result of the different combinations of genes being turned on or off? The possible arrangements are enormous! But if we could map every single cause and effect of the different combinations, and if we could reverse the gene’s state to keep the good while eliminating the bad… then we could hypothetically* cure cancer, slow aging, stop obesity, and so much more.
Source: whatisepigenetics.com





